Grinder-Dressing
As the grinding wheel removes material from the workpiece, it wears out. To ensure the roundness of the grinding wheel, and to maintain the cut shape, a dresser unit is periodically used. This helps to reduce the wear and tear associated with the process.
With the proper dresser device, it is possible to change the grinding wheel diameter or to create a new cross-section profile on the wheel.
Grinder-Dressing Module
VERICUT has a Grinder-Dressing module giving the ability to simulate the process for optimum output on the first try.
The Grinder-Dressing module offers superior G-Code simulation for all manufacturing industries. G-Code simulation provides a virtual representation of a CNC machine's tool path.
Simulating grinding operations with a dressed wheel, allows the user to check and verify all related processes on expensive parts and equipment. This, in turn, can help with reducing manufacturing costs and speeding up associated timelines
The Grinder-Dressing module supports continuous grinding, in-process grinding and creep feed grinding. This range means that the grinding wheel diameter constantly changes during machining. It helps in keeping the grinding wheel in a state of specified sharpness.
The VERICUT verification process accurately checks for errors on all 5-axis milling and turning processes. This applies to all processes, no matter how complex the machining operation is.
- Check dressing operations on the grinding wheel
- Check dressed grinding wheel on the part
- Check continuous dressing during grinding operations
- Check the motion of coolant nozzles for collision
- Check NC handwritten subroutines for dressing subroutines
- Measure and analyse “complex” grinding wheel shape after dressing
- Check grinding wheel size reduction
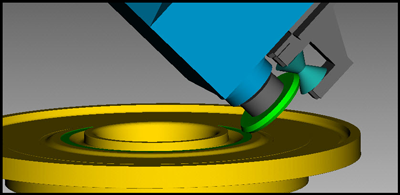
What is wheel grinding?
Wheel grinding refers to a process used in manufacturing where a grinding wheel removes material from a workpiece's surface.
The grinding wheel's abrasive particles on its surface make contact with the workpiece, generating friction and cutting action. This process helps to refine a component's surface by removing unwanted material such as excess metal or stretches.
A wheel grinding machine or general wheel grinding is used in a variety of different industrial manufacturing processes. Wheel grinding is often used in various industries, such as metalworking, automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing, where precision and surface quality are crucial. While this is typically metal-focused wheel grinding, it can be used on ceramics, composites and plastics too.
What can simulating wheel grinding do?
Adding simulation to your wheel grinding processes can have a multitude of benefits.
Cost Savings
Simulation allows manufacturers to optimise grinding processes without the need for physical prototypes or extensive trial-and-error testing. This helps reduce material waste, minimise tool wear, and avoid costly errors.
Process Optimisation
Simulation lets design engineers and process managers find the optimal wheel selection, grinding speed, feed rate, and coolant and lubricant usage.
This analysis can lead to improved surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and overall productivity.
Design Validation
Simulating the process allows designers and engineers to validate their designs. They can assess the manufacturability of the workpiece, identify interference or issues, and make design modifications early in the development stage.
Time Efficiency
Simulation helps in predicting the behaviour of the grinding process and its impact on the workpiece. This saves significant time by eliminating the need for physical trial runs to evaluate different grinding setups.
Safety and Risk Mitigation
Wheel grinding involves potential safety risks the nature of its high-speed rotations. Adding simulation before installation can help identify or prevent safety hazards and evaluate the effectiveness of safety measures.
 Germany
Germany Italy
Italy USA
USA South Korea
South Korea UK
UK India
India France
France China
China Japan
Japan